- Product Details
Keywords
Quick Details
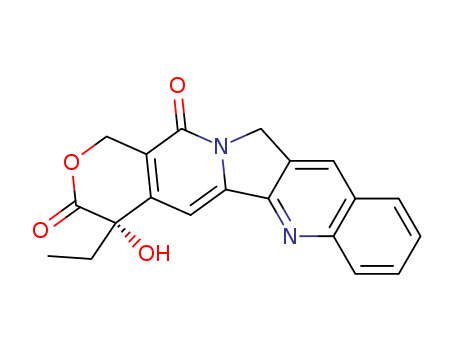
- ProName: (+)-Camptothecin
- CasNo: 7689-03-4
- Molecular Formula: C20H16N2O4
- Appearance: Pale yellow powder
- Application: 9S)-(+)-Camptothecin binds irreversibl...
- DeliveryTime: ASAP
- PackAge: plastic and foil bag
- Port: SHANGHAI
- ProductionCapacity: /
- Purity: >98%
- Storage: Store at or below -20 oC in dry, clean...
- Transportation: By courier, by air, by sea
- LimitNum: 1 Gram
Superiority
Molecular Weight: 348.4 Molecular Formula: C20H16N2O4 Form: Solid Solubility: Soluble in chloroform/m…
Details
- C20H16N2O4
- Solid
- Soluble in chloroform/methanol (4:1) (4 mg/ml), DMSO (10 mg/ml), methanol (40 mg/ml), 0.1N sodium hydroxide (50 mg/ml), and acetic acid. Insoluble in water.
- 260 °C (lit.)(dec.)
- 757.01 °C at 760 mmHg
- 411.63 °C
- 1.51 g/cm3
- n20D 1.75
-
Safety
- UN 1544, Class 6.1, Packing group III
- UQ0492000
- Camptothecin was originally isolated from the stem wood of the Camptotheca acuminata tree and was shown to exhibit antileukemic/antitumour activity, and reversibly inhibit nuclear Topo I (topoisomerase I) by binding to and stabilizing the topoisomerase-DNA covalent complex. Advancing replication forks are believed to interact with these complexes leading to double strand breaks, which is thought to be responsible for much of the cytotoxicity; other research has shown that some of the antitumor activity could be derived from the inhibition of NOS2 (iNOS or inducible nitric oxide synthase) which generates nitric oxide, an important regulator of angiogenesis and other biochemical pathways. The discovery of Camptothecin spurred the development of many derivatives with superior activity and solubility, including Irinotecan (we offer this too) and Topotecan (we offer this too). Although most noted for its anticancer activity, Camptothecin and derivatives have shown other pertinent biochemical actions, including: antiprotozoal, antimalarial, inhibition of HIV, upregulation of p53, and induction of apoptosis. This product also exhibits intense blue fluorescence when exposed to UV light, which could be useful in optical experiments






![3-[(3-Amino-4-methylaminobenzoyl)pyridin-2-ylamino]propionic acid ethyl ester](http://file1.lookchem.com/cas/reactions/2021/05/31/9147567.png)